

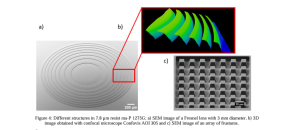
S. Schermer et. al. | Proc. SPIE 12956, Novel Patterning Technologies 2024, April 2024 | Article pdf
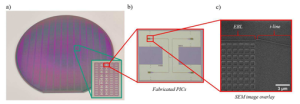
S. Schermer et. al. | Micro and Nano Engineering, Vol. 23, June 2024, 100264 | Article pdf
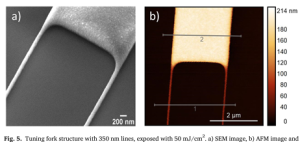
C. Helke et. al. | Micro and Nano Engineering, Vol. 19, June 2023, 100189 | Article pdf
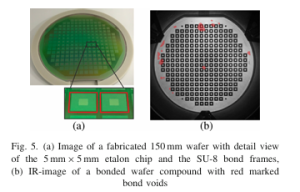
C. Helke et. al. | Micro and Nano Engineering, Vol. 19, June 2023, 100189 | Article pdf

M. Haase et. al. | Proceedings Vol. 12898, Advanced Fabrication Technologies for Micro/Nano Optics and Photonics XVII, March 2024 | Article pdf
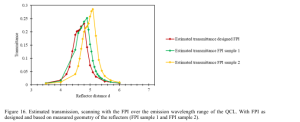
J. Wecker et. al. | Proc. SPIE Vol. 12426, March 2023 | Article pdf
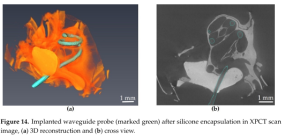
C. Helke et. al. | Materials 2023, 16, 106 | Article pdf
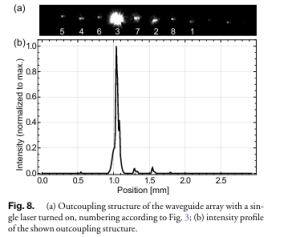
K. Kunze et. al. | Applied Optics Vol. 62, Issue 35, pp. 9353-9360 (2023) | Article pdf
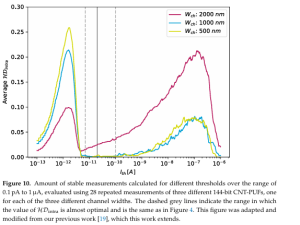
S. Böttger et. al. | Nanomaterials 2023, 13(22), 2930 | Article pdf